Marketplace Architecture & History
A technical retrospective on the evolution of the DarkMatter hidden service, analyzing its cryptographic infrastructure, community growth, and security protocols.
Executive Summary
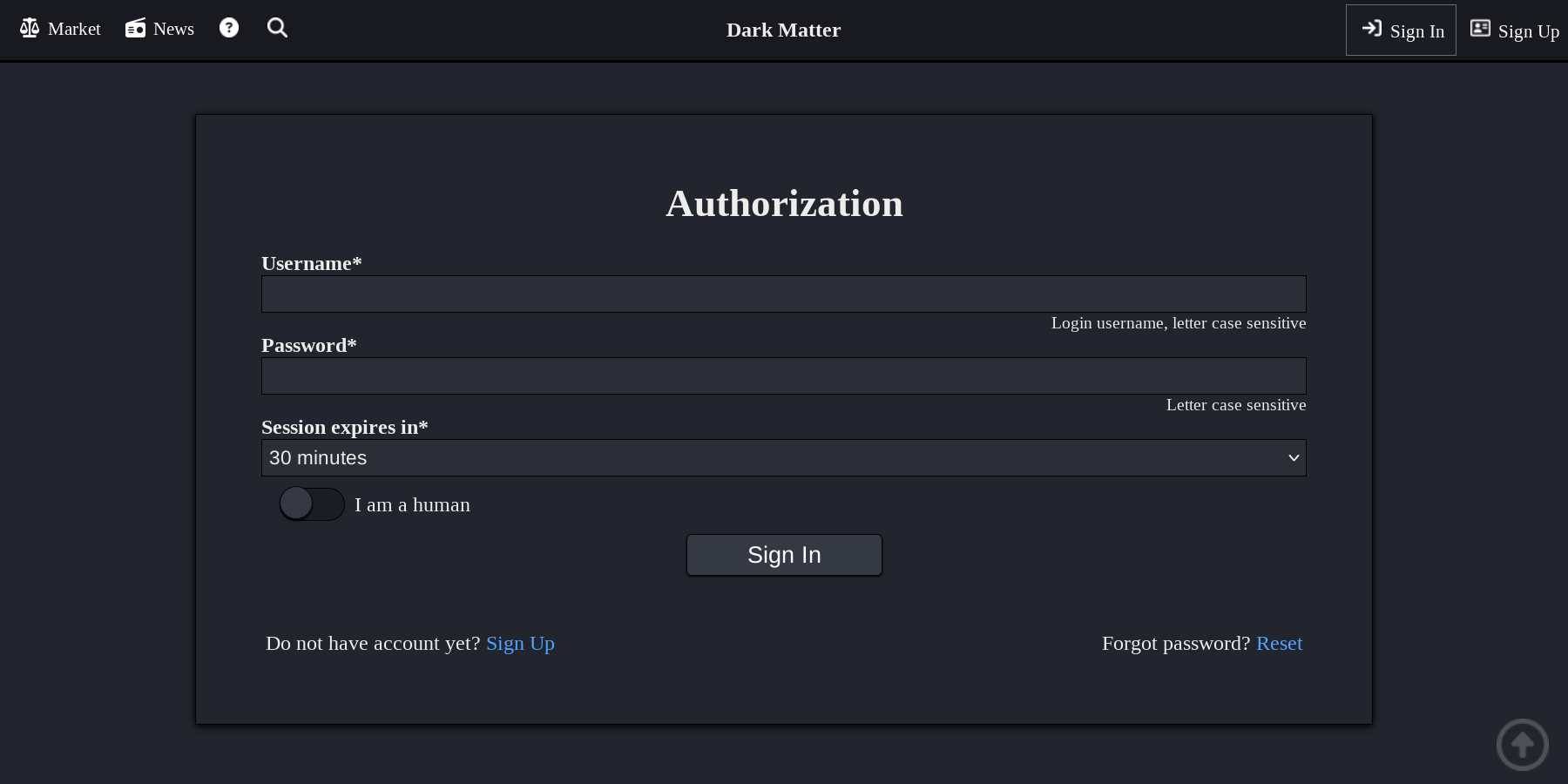
DarkMatter Market Wiki emerged as a notable hidden service within the Tor network ecosystem, designed primarily to facilitate the exchange of digital goods and services using decentralized cryptocurrencies. Established by anonymous developers, the platform distinguishes itself through a rigorous focus on operational security (OpSec) and a minimalist, utilitarian interface that prioritizes speed and encryption over aesthetic flourish.
Unlike earlier generations of darknet markets that relied heavily on Bitcoin, DarkMatter adopted a Monero-first (XMR) approach early in its lifecycle. This architectural decision was driven by the need to mitigate blockchain surveillance analysis, ensuring that transaction graphs remain obfuscated. The platform operates exclusively via the Tor network, utilizing V3 onion services to maintain server anonymity.
Technical Architecture
Cryptographic Security
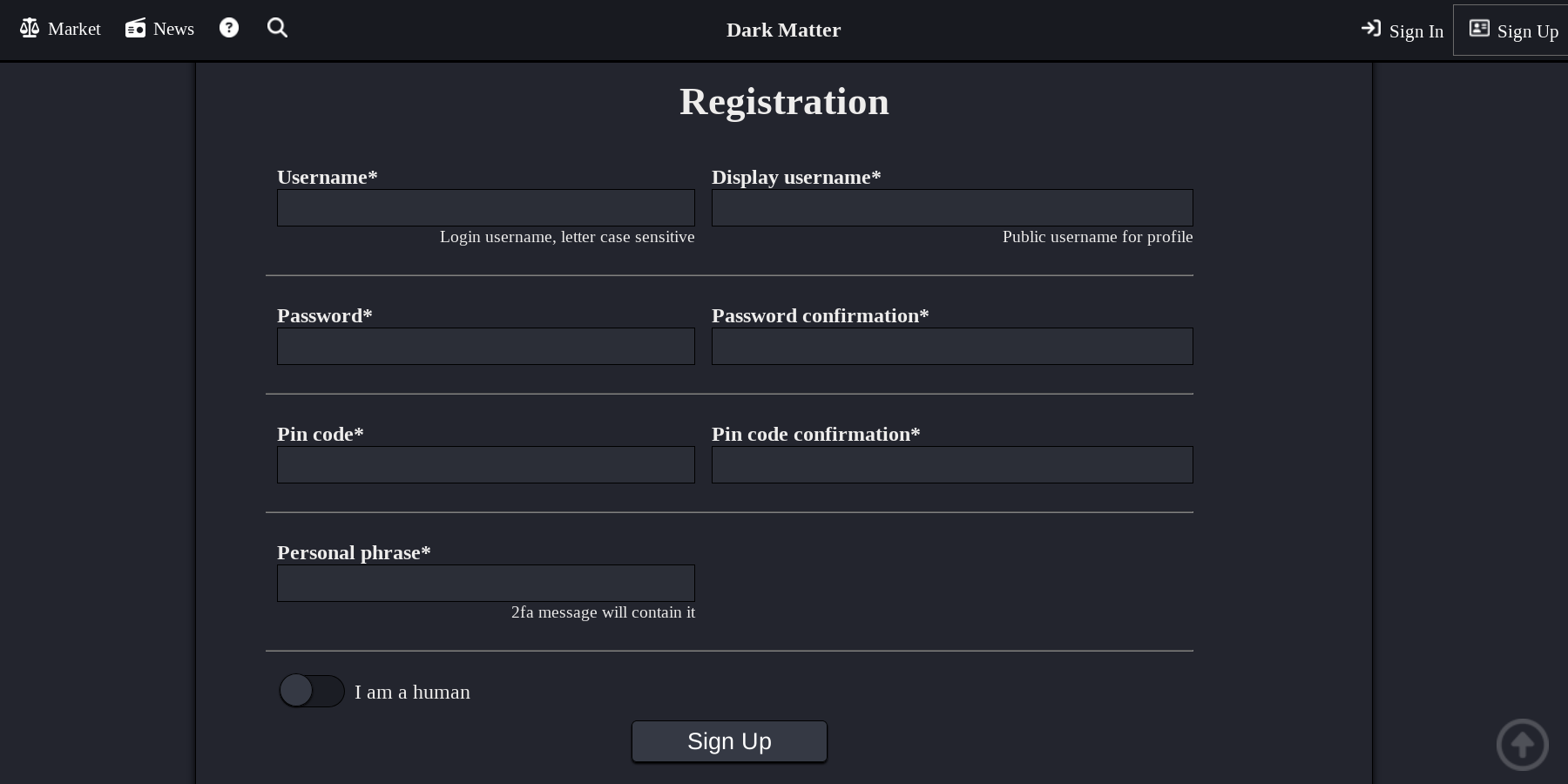
The platform enforces mandatory PGP (Pretty Good Privacy) encryption for all sensitive communications. Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) is required for vendor accounts and optional for standard users, utilizing public key cryptography to verify identity without transmitting passwords.
Escrow Systems
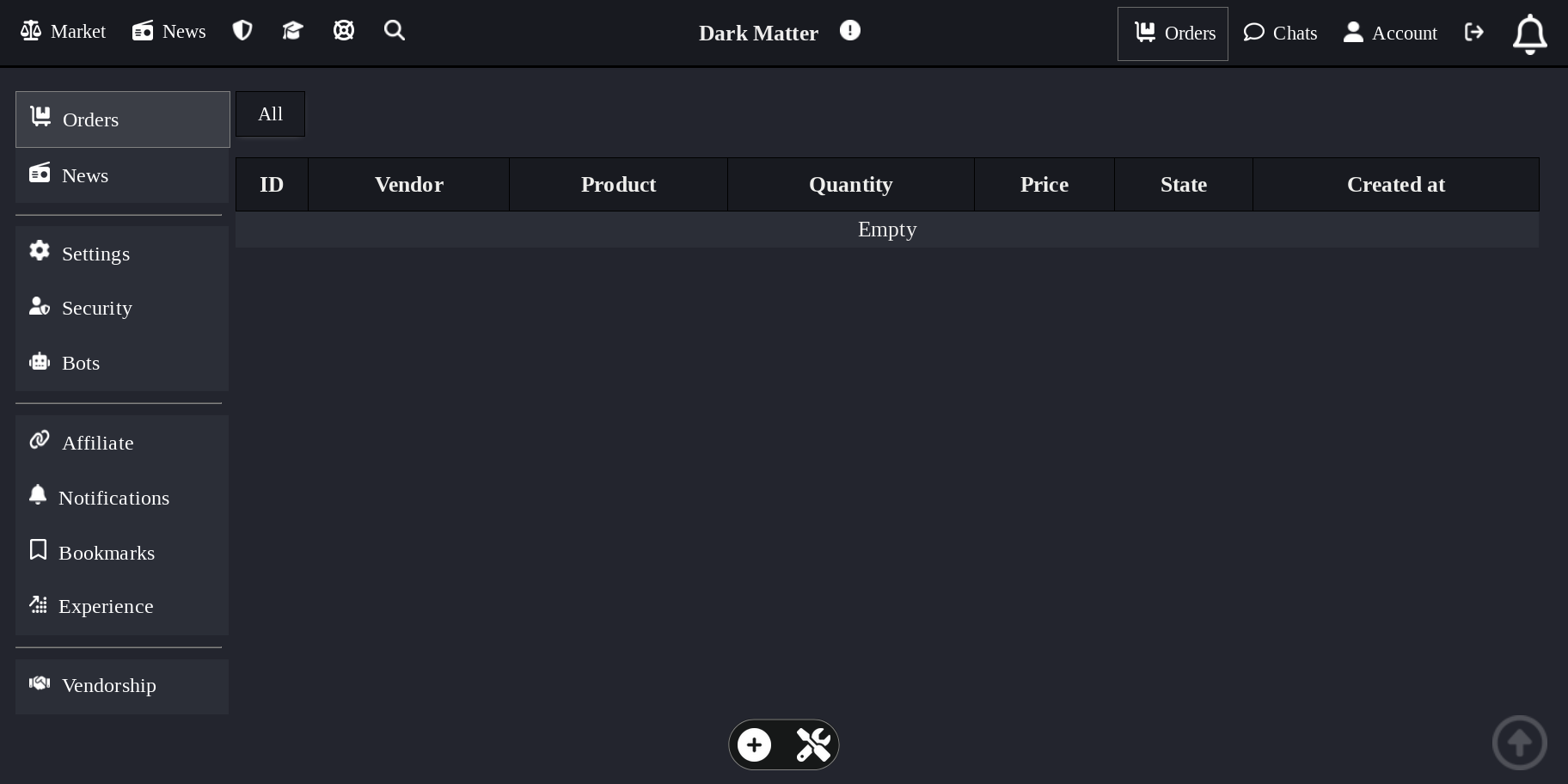
DarkMatter employs a traditional escrow system alongside finalized early (FE) options for established vendors. The escrow logic is server-side, holding funds in temporary operational wallets until delivery is confirmed or a dispute is resolved by platform moderators.
Network Infrastructure
- Tor V3 Onion Services (56-character addresses)
- Distributed Server Load Balancing (Anti-DDoS)
- No JavaScript Requirement (Degrades gracefully)
Community & Ecosystem
Based on public blockchain analysis and forum activity, the user base is estimated to be in the tens of thousands. Vendor verification involves a strict bonding policy, requiring a deposit of XMR to discourage spam and scam listings. The community is largely self-regulated via a reputation feedback system that tracks successful fulfillments and dispute ratios.
Operational Timeline
Initial Deployment
Beta launch of the onion service. Initial stress testing of the XMR wallet integration.
Security Overhaul
Implementation of mandatory 2FA for vendors. Introduction of the automated dispute resolution center.
Infrastructure Expansion
Migration to distributed server architecture to mitigate increasing DDoS attacks on the Tor network.
Stable Operations
Platform operating with 99% uptime. Continued focus on walletless payment research.
Current Status
Interface Architecture Analysis